Hernia
A Hernia is an out-pouching of intra-abdominal contents through a defect, or hole in the abdominal muscles. Hernias can occur anywhere in the abdomen, but most commonly occur at weak points where a small tear can start, and enlarge over time. The common weak points are;
- Inguinal - This is the most common spot in men, in the groin crease
- Femoral – Here the weak point is where the blood vessels to the thigh pass
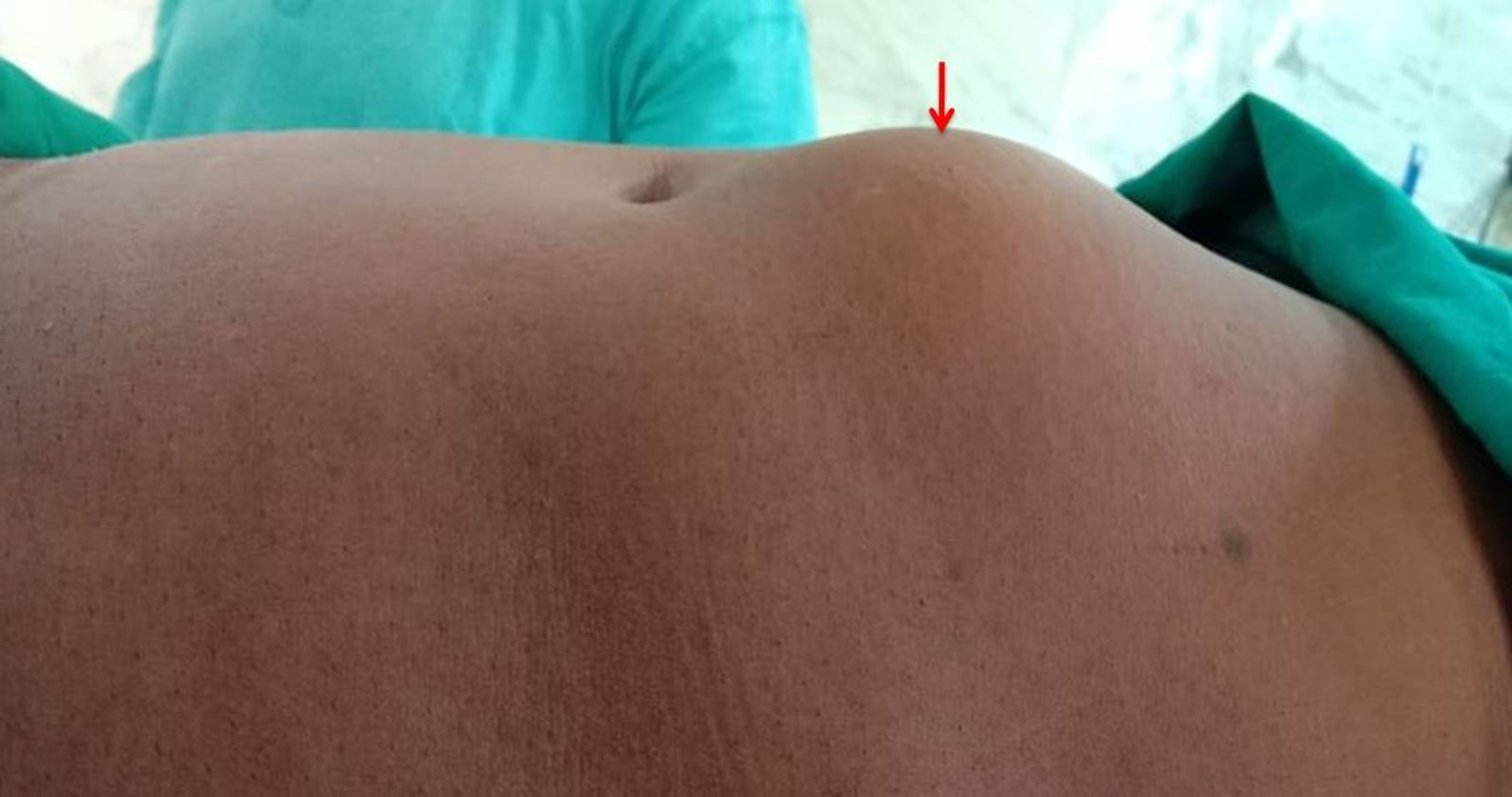
- Umbilical – Hernias around the belly button are common
- Epigastric –The occur in the region between the belly button and the breast bone.
- Incisional – Scar tissue after previous surgery is weaker than the surrounding muscle and can tear to form a hernia.
Symptoms of hernia
- A lump that comes and goes and is more prominent on standing or straining that may get painful.
Complications of Hernias
- Incarceration occurs with a long term (chronic) hernia where the contents come out’ and stay out and are unable to be pushed back in.
- Strangulation is where in the short term the contents come out and cannot be pushed back in, and where the defect causes such pressure on the blood vessels that the contents are starved of blood supply. This causes swelling and severe pain. This is an emergency and warrants prompt attention at hospital. Unless it is dealt with promptly, the contents of the hernia will die which can lead to bowel loss and further complications.
Who needs a hernia repair?
Patients with hernias, who are fit enough to undergo surgery should have hernias repaired before complications occur. Patients with strangulated hernias require urgent repair.
How is the hernia repaired?
The principle of hernia repair is to reduce the contents back into the abdominal cavity and close the muscle. In general; larger defects are best dealt with by placing an artificial mesh over the hole.
It is generally repaired with laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery.
Complex hernias that occur in an old abdominal surgery scar occasionally require a procedure called component separation and abdominoplasty in order to provide a better anchorage to the mesh and also a good cosmetic result.
The postoperative course
The postoperative course is different for each person. Most patients stay one night in hospital. Sutures are dissolving and buried, dressings can stay on for 7 days. A follow-up appointment is made after 5 days. You may eat and drink normally, and walk around straight away. Heavy lifting and vigorous sports should be avoided for 6 weeks after the surgery.